 Relevancy and Engagement
minnesota.agclassroom.org
Relevancy and Engagement
minnesota.agclassroom.org
Bring Home the Blue, Not the Flu! (Grades 9-12)
Grade Level
Purpose
Using the context of a county fair livestock show, students investigate how diseases are spread. With a focus on zoonotic disease, students will complete simulations demonstrating the spread of illness and implementation of biosecurity measures as well as complete an online module to deepen understanding of specific diseases and their prevention. Grades 9-12
Estimated Time
Materials Needed
Interest Approach:
- How do Germs Spread? infographic
Activity 1: What is a Zoonotic Disease?
Activity 2: Disease Transmission and Outbreak Simulation
- Numbered clear plastic cups, 1 per student
- Numbered nametags (stickers)
- Behavior Cards
- Nitrile gloves, 1 pair per student
- Distilled water
- Distilled water with baking soda
- Phenol red
- Dropper
- Permanent marker
- Outbreak Investigation activity packets, 1 per student
- Bubble blower and bubbles
Activity 3: Animal Biosecurity Simulation
- Glo Germ powder
- Black light
- Stuffed farm animals (sheep, cattle, goats, horses, and/or hogs) covered in Glo Germ powder, 1 per group
- Feed samples mixed with Glo Germ powder in bags
- Buckets, 1 per group
- Objects that can serve as fomites (brushes, halters, etc.) covered in Glo Germ powder
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, shoe covers, coveralls, face mask, etc.
Activity 4: Bring Home the Blue, Not the Flu Online Modules
- Bring Home the Blue, Not the Flu! online modules
Vocabulary
aerosol: a suspension of fine solid or liquid particles in gas
contaminate: to make something dirty or impure by accidentally or purposely adding something harmful
disease: a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism
fomite: objects or materials which are likely to carry infection, such as clothes, utensils, and furniture
germ: a microorganism causing disease
ingestion: consuming something orally
pathogen: a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease
transmission: the act or process by which something is spread or passed from one person or thing to another
vector-borne transmission: infection transmitted to humans and other animals by blood-feeding anthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas
Did You Know?
- There are many jobs that help protect human and animal health including veterinarians, physicians, nurses, laboratory scientists, and epidemiologists.
- Three out of four new or emerging infectious diseases in people come from an animal source.1
- Scientists estimate that more than 6 out of every 10 known infectious diseases in people can be spread from animals.1
- Washing your hands is the simplest and most effective ways to prevent disease.1
Background Agricultural Connections
Bring Home the Blue, Not the Flu! is a program developed at Iowa State University to educate youth about zoonotic diseases, how they are transmitted, and what can be done to prevent the spread of illness from animals to humans.
Some people are carriers of disease. Initially, these carriers may appear healthy or show only mild signs of disease. At some point they may eventually get sick, but they may not be recognized as having the disease until they've exposed and infected others. This is one reason why some pathogens can spread so quickly.
Diseases can be spread by direct contact, indirect contact, aerosols or droplets, ingestion or oral transmission, or vectors. Indirect contact transmission is the spread of pathogens through coming into contact with areas where animals live or roam, or objects or surfaces contaminated by an infected animal. Objects or surfaces that may become contaminated with pathogens are called fomites. Some examples of fomites are boots, cages, needles, bedding, clothing, vehicles, and restraint devices. Ingestion or oral transmission occurs when disease-causing agents are ingested from contaminated food or water or by licking or chewing contaminated objects in the environment. Germs can be present even when things (clothing, gloves, shoes, equipment, etc.) appear clean or when animals appear healthy.
Ways to prevent direct contact disease transmission:
- Isolate sick animals
- Wear gloves when working with sick animals
- Wash your hands after having contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
Ways to prevent indirect contact disease transmission:
- Avoid sharing equipment, or clean and disinfect equipment when sharing is necessary
- Clean and disinfect any equipment used with sick animals or animals with skin lesions
- Dispose of or wash boots and clothing after animal contact
- Wash your hands after having contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
Ways to prevent aerosol disease transmission:
- Increase distance between sick animals and healthy animals and people
- Wear respiratory protection when working with sick animals
- Provide fresh air to animals and people
- Decrease humidity and odor buildup in barns
- Stay away from animal barns if you are sick
Ways to prevent oral disease transmission:
- Wash your hands
- After contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
- After cleaning pens or contact with manure
- Before preparing or handling food
- After going to the bathroom
- Cook meat to the appropriate temperature
- Store food at the appropriate temperature
Ways to prevent vector-borne disease transmission:
- Use insect control products
- Work with your veterinarian to check and treat your animals for parasites
- Prevent standing water
- Check for ticks on people and pets
Engage
- Ask students to help you brainstorm all of the places that humans come into contact with animals. Make a list on the board as students brainstorm. Farms, zoos, petting zoos, pets in our homes, county fairs, and various animal/livestock shows are a few examples they could come up with.
- Define infectious disease as an illness that is caused by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Give examples of infectious diseases that students will be familiar with (Rhinovirus causes the common cold, there are various forms of flu viruses, pneumonia is often caused by a bacterial infection of the lungs, and athlete's foot is a fungal infection on the feet.)
- Ask students, "How do infectious diseases spread? Project the How do Germs Spread? infographic. Explain that "germ" is a general term for a disease-causing agent like a virus, bacteria, fungus or protozoa.
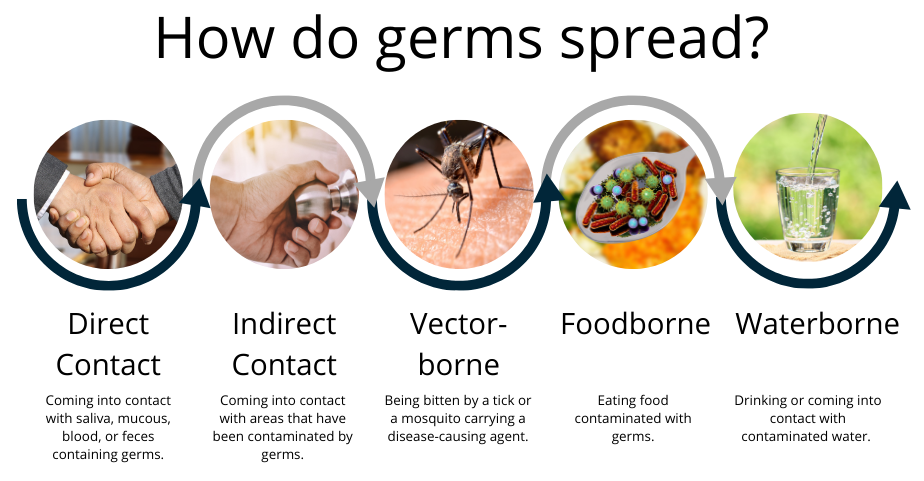

- Ask students, "Can disease-causing germs spread from animals to people?" Explain that we will be exploring this question.
Explore and Explain
Activity 1: What is a zoonotic disease?
- Define the word zoonotic with students. Write the word and its definition on the board.
- Watch the video clip, How do viruses jump from animals to humans? Pause the video at 0:57 and emphasize the fact that most viruses are species-specific and don't move from species to species. However, when they do it can give way to deadly epidemics. Continue the video to learn more about the science of viral transmission from one species to another.
| Terms such as "Swine Flu" or "Bird Flu" can lead to the misconception that someone who consumes meat from a pig or eggs from a chicken (bird) could get the flu. Throughout the lesson, reinforce the science of virus transmission through live animal contact to correct these misconceptions. |
Activity 2: Disease Transmission and Outbreak Simulation
Teacher Preparation: Half fill 10% of the cups with baking soda water. (For example, if there are 20 students, fill 2 cups with baking soda water). Half fill the remaining cups with distilled water. Place numbered nametags with the corresponding cup. Make note of which cups contain baking soda water. Set a Behavior Card under each cup. Pair the baking soda cups with a "Participants in multiple open, county, and state shows" card. Watch the instruction video below for more illustration.
Alternative Materials: Yellow food coloring (uninfected) and blue food coloring (infected) may be used instead of baking soda and phenol red. Any shade of green will represent infection at the end of the swapping activity, and may better demonstrate varying severity of illness. These materials may be easier to obtain.
- Ask students if they remember where the swine flu was spread in the example used at the beginning of the video clip from Activity 1. (A county fair)
- Provide the following explanation to students before beginning the simulation:
- Some people and animals carry disease-causing pathogens (viruses or bacteria). Initially, these carriers appear healthy or show only mild signs of sickness. At some point they may get sick, but oftentimes they have already exposed and infected others. This activity is designed to simulate the uncontrolled spread of a disease through a population. Each of you will have a cup that is half-filled with water. One or two of you will have a cup that contains baking soda water. The students with the baking soda water will represent the original carrier(s) of the simulated disease. The original carrier(s) will make contact with other participants who will make contact with others to represent normal activities at a county fair. At the end of the simulation, everyone will be tested to see who has become infected and we'll discuss how to trace the infection back to its source.
- Provide each student with one cup, the associated Behavior Card, the corresponding numbered nametag, and an Outbreak Investigation activity packet.
- Instruct students to put on their numbered nametag and review their behavior card. Tell them that they will be swapping fluids with other participants and each fluid swap should occur with a different person.
- Ask students to move about the room and exchange fluids according to the instructions on their behavior card.
- To exchange fluids, one person will dump all of the contents of their cup into the other person's cup.
- Return half of the solution back to the empty cup. (Demonstrate with two water cups.)
- Record the number of the person they exchanged with on their "Fluid Swap Record" in their packet.
- Students should repeat step 4 as many times as specified on their behavior card. Remind students that each swap should be with someone they haven't already swapped with, and that they should only swap as many times as their behavior card indicates.
- When swapping has finished, instruct students to return to their desks with their cups.
- Add 2-3 drops of phenol red to each cup. A pink color change (bright or faint) indicates a positive result—this person is now considered "infected." No color change is "uninfected."
- Work with the class to fill out Table 1 in their packets. Ask all with one exposure to raise their hands or stand. Discuss mild to severe infection and individuals who are at risk of severe complications (pregnant, very young or old, immunocompromised). Have the students answer questions 2 and 3 individually before discussing as a class.
- Ask the students, "How did the number of people infected increase with each round of interactions?" Assuming one person was initially infected, fill out Table 4 and Graph 5 in the student in the student activity packet.
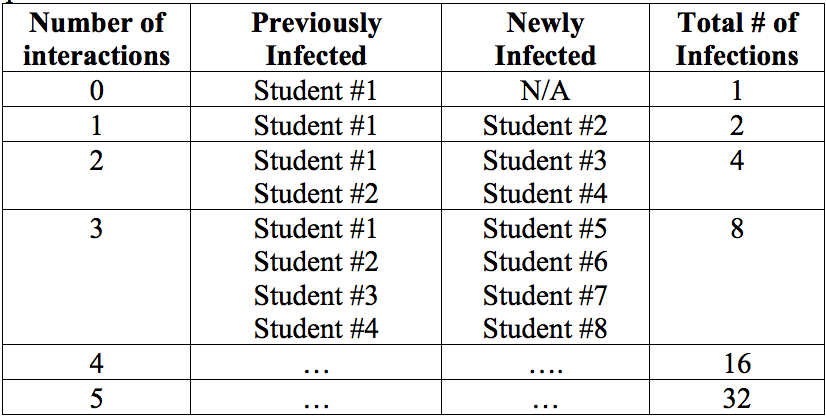
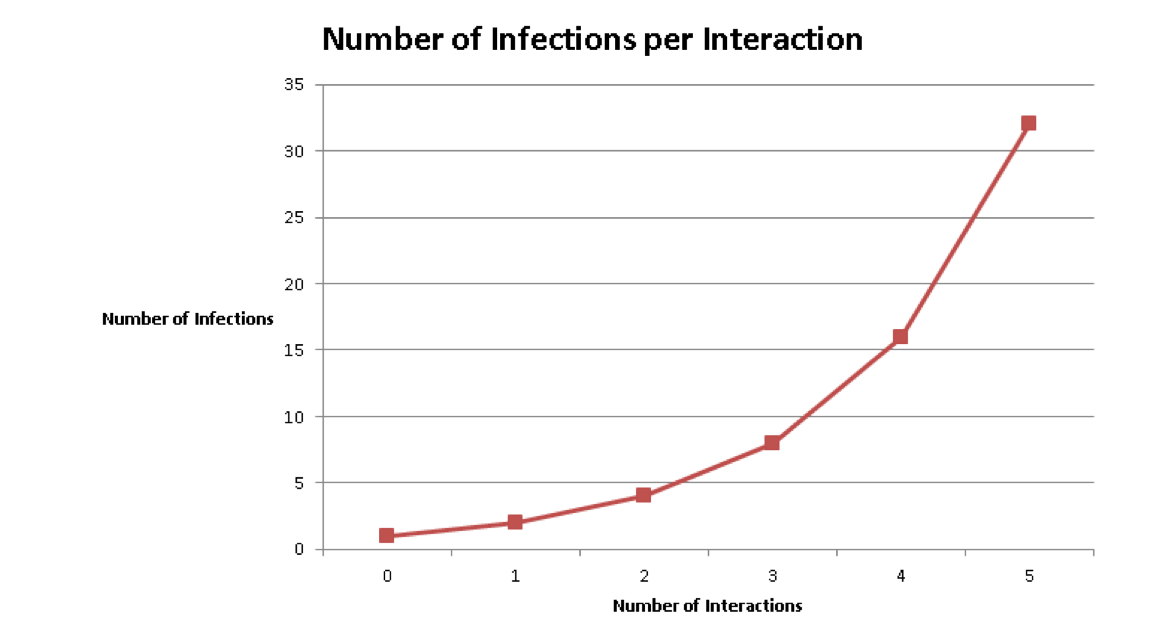
- Have the students answer questions 6 and 7 individually and then discuss:
- What do you notice about the rate of increase in the number of infections? (Discuss the doubling of number of infections in each round.)
- Does the graph show linear or exponential growth? (exponential growth)
- If we did this activity long enough, would everyone become infected? Why or why not? (Yes, but the doubling of infection we see in each generation does not continue indefinitely. In the beginning the curve increases exponentially, but then levels out. This pattern is known as logistic growth curve (S-curve). As the number of infected participants increases, it becomes increasingly more likely that an infected participant interacts with another participant that has already been infected. As a result, the number of new infections slows down. This type of growth also assumes that no one has any protection from the infection, such as vaccination.)
- Ask the class, "How can we determine who was the original source of infection?" Discuss the idea that it's important for participants to realize that if they are infected, but can identify people they swapped with that AREN'T infected, then they could not have been the original source. Working through this should lead back to the people that were originally infected and those that they infected after the first swap.
- After the discussion, have all "infected" participants stand up and "non-infected" participants remain seated. "Infected" participants should look around at "non-infected" participants. If anyone they exchanged fluids with is sitting, they should sit down as well. Continue this until there are 7-10 participants still standing. Direct the remaining participants to bring their list of people they swapped with to the front of the room and complete the "infection tree" as a class. Students have an "infection tree" in their packet that they can fill out as the group discusses. Completing the tree will require input from participants that remain seated.
- Once the tree is complete, shade in all bubbles representing people that were "infected" at the end of the activity. Use this diagram to discuss and identify the probable initial source of the infection. Teacher Note: You will only be able to narrow it down to twice as many "suspects" as there were initial infected cups (e.g., starting with two cups means you'll be left with four suspects).
- Activity Adaptation: Rather than using the "infection tree" to identify the initial source of infection, simply use the "stand up/sit down" method:
- Have everyone stand up that is infected at the end of the activity.
- If anyone standing up swapped fluids with anyone that is still sitting (uninfected), they should sit down.
- Continue this until you're left with twice the number of people standing as you had initially infected cups.
- One infected cup would result in two people left standing at the end. In this activity, there is no way to determine which person was the original source of infection, but you can share that information with the group.
- Ask the class, "In a real investigation, how could we distinguish between who was the original source and who they infected? Why can't we do that here?" (In this activity, the potential first exposure to disease for everyone was the same when you were randomly handed a cup that either had water or a baking soda solution. You can't use earlier exposure or timeline to further narrow down who was originally infected and spread the "disease" to the rest of the group.)
- Ask the students, "How would this investigation be different if you hadn't kept notes about whom you swapped fluids with and in what order?" Have them answer question 9 individually before discussing that one of the difficulties of a true outbreak investigation is that people's memories aren't always that great. It typically takes time for a disease to appear after initial exposure, and it takes even more time for an epidemiological investigation.
- Ask, "What preventative measures could have been taken to avoid exposure to the disease?" (Lots of possible answers, including vaccination, attending fewer shows, etc.)
- Ask the class, "How would an airborne disease spread differently? Why?" (In this activity, disease spread was dependent on a very direct, one-on-one interaction. Airborne diseases are able to spread more easily and indirectly from person to person, animal to animal, or animal to person and it often isn't clear when you've been exposed to someone with the disease. In this activity, it was very clear whom you swapped liquids with. It's much more difficult to track who you simply walk by, were in the barn with at the same time, etc.)
- Use a bubble blower and see who gets hit with a bubble to model airborne disease spread. Explain that airborne disease spread requires less movement. Some diseases can be transmitted in the air for long distances.
Activity 2: Animal Biosecurity Simulation
Teacher Preparation: Watch the instruction video to illustrate the activity.
- Explain to the class that the word biosecurity describes procedures intended to protect humans or animals against disease or harmful biological agents. They are going to simulate some common activities that might take place at a county fair livestock show.
- If students are unfamiliar with livestock shows commonly held at county fairs, watch FFA & 4-H Students Show Skills at Junior National Livestock Show to gain familiarity.
- Divide the class into small groups. Provide each group with a stuffed animal, feed samples, and a bucket. Place the show equipment on a table. Explain to the groups that they need to get their animal ready for a show by completing the following tasks:
- "Inspect" the animal to make sure it is ready for the show.
- Mix different feed samples in the bucket.
- Collect the equipment to bring to the show.
- Shine a black light on each student's hands to demonstrate how diseases can be spread by direct contact and from touching clothing, feed, buckets, equipment, fair food, etc. Demonstrate how pathogens can be spread by shoes by shining the black light throughout the room where students walked.
- Discuss the importance of handwashing and how and when to wash hands to prevent the spread of disease. Share the Five Steps to Wash Your Hands the Right Way:
- Wet your hands with clean, running water (warm or cold), turn off the tap, and apply soap.
- Lather your hands by rubbing them together with the soap. Lather the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails.
- Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds. Need a timer? Hum the "Happy Birthday" song from beginning to end twice.
- Rinse your hands well under clean, running water.
- Dry your hands using a clean towel or air dry them.
- Have the students wash their hands and then use the black light again.
- Invite the students to put on personal protective equipment (PPE) and repeat steps 4 and 5.
- Discuss how wearing PPE helps to prevent disease transmission.
- Use the information in the Background Agricultural Connections section to discuss ways to prevent direct contact, indirect contact, aerosol, oral, and vector-borne (infection transmitted to humans and other animals by blood-feeding anthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) transmission.
Activity 4: Bring Home the Blue and Not the Flu! Interactive Modules
- Direct students to the Bring Home the Blue, Not the Flu! online modules. Instruct them to complete each module:
- Module 1: Introduction to Influenza, Zoonoses, and Disease Risks
- Module 2: Zoonotic Disease Transmission
- Module 3: Zoonotic Disease Prevention and Biosecurity
- Module 4: Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Outbreak Case Study
- Module 5: Influenza A Virus of Swine Origin (H3N2v) Outbreak Case Study
- Module 6: One Health Agencies and Careers
Evaluate
After conducting these activities, review and summarize the following key concepts:
- Washing your hands is one of the simplest and most effective ways to fight germs that cause disease.
- A zoonotic disease is one that can be transmitted from animals to humans.
- Biosecurity measures outline protocol to decrease the transmission of disease-causing pathogens.
Sources
- https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/zoonotic-diseases.html
Acknowledgements
- The Interest Approach and Activity 1 were added by the National Center for Agricultural Literacy
- Activity 2 instructions were adapted from an activity developed by the Indiana State Department of Health.